MySql default configurations in GCP cloud and in Azure cloud

We recently had a late-night memory troubleshooting session on MySQL in the GCP cloud.
I am sharing with you my MySQL learning outcomes and review of GCP default Cloud MySQL configuration related to performance and memory management.
I will go over the main MySQL performance configuration parameters and what the GCP defaults are. I have also looked up Azure defaults to see if there are any differences.
GCP Cloud MySQL configurations seem to favour writing workloads.
On Azure Database for Flexible server, some parameters are not present, for instance, making unique_checks and foreign_key_checks disabled.
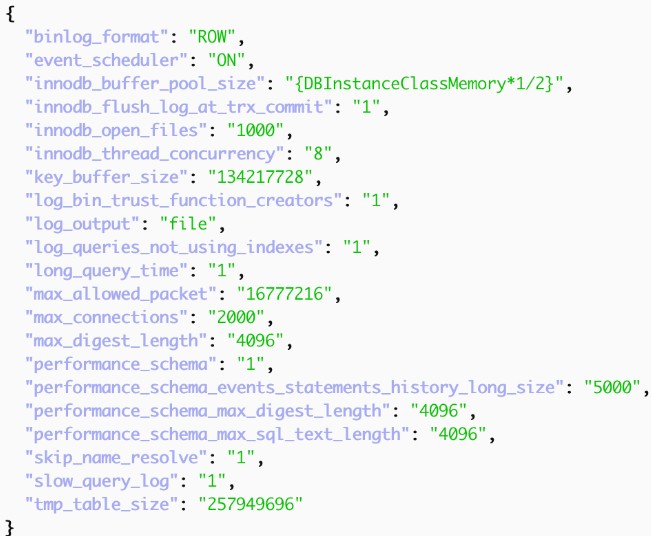
innodb_buffer_pool_size
What it is & best practices: Memory area where InnoDB caches table and index data. Best practice: ~80% of instance memory (can be smaller if you only use a small fraction of your data).
GCP default: 70% of total instance memory
Azure default: 25% of total instance memory
innodb_log_file_size
What it is & best practices: Redo log, applied after reboot; impacts recovery time. MySQL default is 128MB; the general suggestion is at least 600MB.
GCP default: 1.17%
Azure default: N/A
innodb_log_buffer_size
What it is & best practices: Buffer size for InnoDB redo log writes. Default 16MB is good for most workloads. If Innodb_log_waits > 0, increase this value.
GCP default: 16MB
Azure default: 4MB
key_buffer_size
What it is & best practices: Buffer size for MyISAM table index blocks. Not used by InnoDB. If only using InnoDB: set to a minimum of 8MB (or 16MB to avoid issues).
GCP default: 8MB
Azure default: 8MB
innodb_doublewrite_batch_size
What it is & best practices: Number of doublewrite pages written in a batch; protects against partial page writes during crashes. MySQL default and best practice: 0 for most workloads.
GCP default: 0
Azure default: 0
max_allowed_packet
What it is & best practices: Maximum size of a single packet/query/row that can be sent to or from the server. Protects against bad queries and huge packets. MySQL default: 64MB.
GCP default: 32MB
Azure default: 16MB
innodb_log_files_in_group
What it is & best practices: Number of redo log files (important for crash recovery). If one is full, you should have a second one.
GCP default: 2
Azure default: N/A
innodb_change_buffering
What it is & best practices: Memory structure used for caching changes in secondary index pages, not in the buffer pool; reduces IO used to keep indexes up-to-date. MySQL default: ALL. General suggestion: NONE because ALL can cause very long shutdown times.
GCP default: all
Azure default: all
innodb_io_capacity
What it is & best practices: Controls the number of IO operations per second that InnoDB can perform for background tasks. Default: 200. For heavy insert/update/delete workloads, 1000 is suggested.
GCP default: 5000 on 64GB RAM, 10000 on 128GB RAM (both with 10K IOPS provisioned)
Azure default: 200
innodb_stats_persistent
What it is & best practices: Controls whether table and index statistics are stored on disk. If not stored, they must be recalculated frequently and after a restart, causing overhead. Suggested: ON.
GCP default: ON
Azure default: ON
innodb_thread_concurrency
What it is & best practices: Used when active threads are much more than available CPUs; can help process more sessions if many are idle. MySQL default: 0 (infinite concurrency). Limits threads inside InnoDB, not connections; change with caution.
GCP default: 0
Azure default: 0
innodb_flash_log_at_trx_commit
What it is & best practices: Controls how frequently the log is flushed to disk. Affects performance vs durability and can be a source of corruption risk.
0: buffer written and flushed once per second
1: flushed every time a transaction is committed (default)
2: written at commit, flushed once per second
With 0 or 2, MySQL does not guarantee full ACID.
GCP default: 1
Azure default: N/A
tmp_table_size / max_heap_table_size
What it is & best practices: Internal temp tables; when they grow too big, they convert from in-memory to on-disk. MySQL uses the smaller of the two. On-disk operations are slow; it's important to tune for complex/long-running queries (you’ll see high write IOPs and disk queue depth). Default: 16MB. Can be increased to 64MB or more.
GCP default: 16MB
Azure default: 16MB
foreign_key_checks / unique_checks
What it is & best practices: Foreign key and unique checks slow down data imports and can be temporarily disabled for bulk operations. Default: ON.
GCP default: ON
Azure default: N/A
optimizer_switch
What it is & best practices: Controls query optimiser behaviour.
GCP default:
index_merge=on, index_merge_union=on, index_merge_sort_union=on, index_merge_intersection=on, engine_condition_pushdown=on, index_condition_pushdown=on, mrr=on, mrr_cost_based=on, block_nested_loop=on, batched_key_access=off, materialization=on, semijoin=on, loosescan=on, firstmatch=on, duplicateweedout=on, subquery_materialization_cost_based=on, use_index_extensions=on, condition_fanout_filter=on, derived_merge=on, use_invisible_indexes=off, skip_scan=on, hash_join=on, subquery_to_derived=off, prefer_ordering_index=on, hypergraph_optimizer=off, derived_condition_pushdown=on
Azure default:
Same as GCP
sql_mode
What it is & best practices: Impacts how MySQL processes SQL: data validation, syntax rules, error handling, GROUP BY behaviour, etc.
GCP default: ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY, STRICT_TRANS_TABLES, NO_ZERO_IN_DATE, NO_ZERO_DATE, ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO, NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
Azure default: Same as GCP
innodb_read_io_threads / innodb_write_io_threads
What it is & best practices: Impacts IO concurrency. Defaults: 4 each. Can increase IO threads (esp. for writes) to keep reads responsive under heavy write workloads.
GCP default: innodb_read_io_threads = 4, innodb_write_io_threads = 8 (favours writes)
Azure default: innodb_read_io_threads = 4, innodb_write_io_threads = 4
innodb_status_output_locks
What it is & best practices: Enables/disables lock monitoring. MySQL default: 0.
GCP default: OFF
Azure default: OFF
table_open_cache
What it is & best practices: Number of open/cached tables; this is the maximum number of table definitions in the cache. Opening a table is expensive, so most tables should fit here. Best practice: ~2× total number of tables.
GCP default: 4000
Azure default: 600
thread_cache_size
What it is & best practices: How many connection threads are cached for reuse; thread creation/destruction is expensive. MySQL default: 14. For applications with big connection peaks, increase this.
GCP default: 100
Azure default: 9
read_rnd_buffer_size
What it is & best practices: Buffer used when reading rows in sorted order after a sort (e.g. ORDER BY). Allocated per connection that needs it. MySQL default: 256KB.
GCP default: 256KB
Azure default: 256KB
read_buffer_size
What it is & best practices: Buffer for sequential table scans. Allocated per connection per table scan. MySQL default: 128KB.
GCP default: 128KB
Azure default: 128KB
innodb_flushing_avg_loops
What it is & best practices: Controls how smoothly InnoDB flushes pages from the buffer pool to disk. MySQL default: 30. Lower (15–20) = more aggressive flushing, faster response to write spikes.
GCP default: 5 (again, seems tuned to speed up writes)
Azure default: 30
host_cache_size
What it is & best practices: Size of host cache used to speed up hostname resolution. MySQL default: min(128 + @@max_connections, 2000). Best practice: enable skip_name_resolve=1 and set host_cache_size=0 to avoid DNS lookups.
GCP default: 703 (note: observed, not noticed changing with max_connections)
Azure default: 279


Comments
No comments yet.
Leave a comment