The Scripts I Use to Compare MySQL Configs in AWS, Azure, and GCP
This blog post will solve a practical “headache” of cross-cloud MySQL configuration audit.
When migrating MySQL databases from cloud to cloud, we sometimes need to compare MySQL parameters between database instances. To see why performance is different or to make sure the data store was migrated alongside the correct configurations.
The most useful tool for this purpose would be to use Cloud CLI, export data to a file, and either compare manually or feed it to AI.
Cloud CLI’s export data defaults are very different between AWS, GCP or Azure, which makes visual comparison confusing, and sometimes AI can also produce wrong conclusions.
I will share my scripts for each cloud, which export all MySQL parameters in a nicely aligned and readable, key:value json, as below:
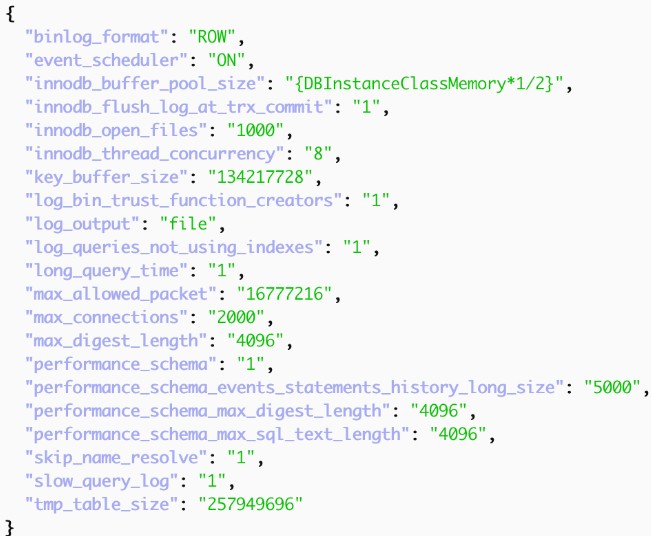
AWS cloud
In AWS RDS, MySQL configurations are managed via 'Parameter Groups'—standalone objects that can be applied to multiple database instances. The following command retrieves only the parameters within a specific group that have been modified from their default values.
db_param_group_name="rds-param-group-name"
aws rds describe-db-parameters \
--db-parameter-group-name $db_param_group_name \
--query "Parameters[?IsModifiable && Source=='user'].[ParameterName,ParameterValue]" \
--output json \
| jq 'map({(.[0]): .[1]}) | add' >> ~/Downloads/aws_rds_params.json
GCP cloud
In GCP Cloud, MySQL parameters are bound to a specific instance, so this will be GCP CLI command that produces an output in the same format
sql_instance="my-sql-instance-name"
gcloud sql instances describe $sql_instance \
--format=json \
| jq '(.settings.databaseFlags // []) | map({(.name): (.value // null)}) | add' >> ~/Downloads/gcp_params.json
Azure cloud
To achieve a similar result in Azure for MySQL Flexible Server, we will use AZ CLI. In Azure, as well as in GCP, MySQL parameters are defined per instance. By default, the "parameter list" command will print all MySQL parameters, and I only wanted to see parameters that were overridden so I added filter --query "[?source=='user-override'].{name:name, value:value}", if you want all parameters, use --query "[].{name:name, value:value}"
Note, the $sql_instance (--server-name) parameter expects just the short name (e.g., my-server), not the full login server name (e.g., my-server.mysql.database.azure.com)
rg="resource_group_name"
sql_instance="server_name"
az mysql flexible-server parameter list \
--resource-group "$rg" \
--server-name "$sql_instance" \
--query "[?source=='user-override'].{name:name, value:value}" \
-o json \
| jq 'map({(.name): (.value // null)}) | add' >> ~/Downloads/azure_params.json



Comments
No comments yet.
Leave a comment